When trading in the forex market one should have good knowledge of the different types of orders and how and when to use them. The order reflects the trader’s intentions for entering and exiting the trade, so their precision can mean the difference between a profit and a loss.
Multiple actions can be included in the same order, for example a level for entry and rules for exit. There are many types of orders, offered by the different forex brokers, but these basic types can be considered most common.
MARKET ORDERS IN THE FOREX MARKET
Market orders are the simplest order type. It means buying or selling the currency pair at the current ask or bid price (respectively). They are executed immediately, at the best available price.
Depending on the market liquidity and volatility, these orders can be subject to slippage. This means that the execution price might be different (better or worse) than the market price at the moment of the order placement.
BUY ORDER
The Buy order is an order to immediately buy the currency pair, at the best available price. This order opens a long position and because it is a market order, it can be executed with slippage.
SELL ORDER
The Sell order is an order to immediately sell the currency pair at the best available price. It can be used for opening a short position and because it is a market order, it can incur slippage.
PENDING ORDERS IN THE FOREX MARKET
Pending orders are the most commonly used order type. They are not directly executed, like market orders, but rather give instructions for opening an order at a price level, defined by the trader.
If the price does not reach the pre-defined level of the pending order, it will not be executed.
Most trading platforms make it very simple and intuitive to enter a pending order. There are four main types available on all platforms.
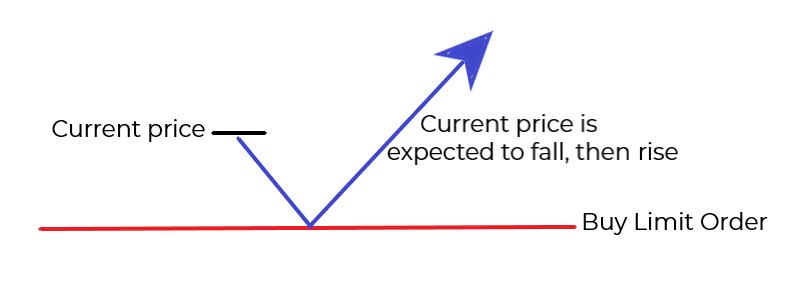
BUY LIMIT ORDER
The Buy Limit is used to buy a currency pair at a level below the current price. It is an opportunity to open a long position at a better price compared to the present.
A Buy limit order is placed below the current market price when you expect it to fall to the limit order level and then to start rising.
SELL LIMIT ORDER
The Sell Limit is used to sell a currency pair at a level above the current price. It is an opportunity to open a short position at a better price compared to the present.
A Sell limit order is used when you expect the current market price to rise to the limit order level and then to start falling.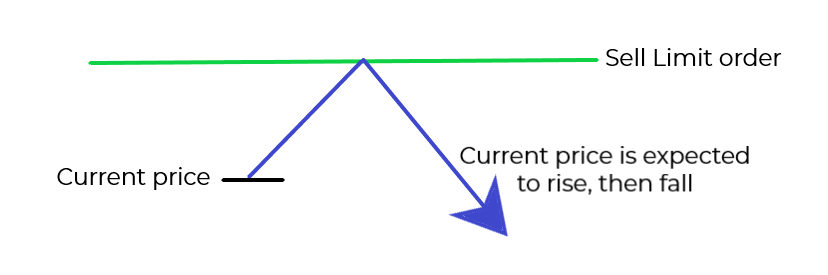
BUY STOP ORDER
The Buy Stop is a pending order to buy a currency pair (open a long position) at a level, which is above the current price. This order gives instructions to open a position at a price worse than the present, so it is used when the trader expects the price to continue up.
A typical situation to use the Buy Stop is at a breakout of a resistance level, when it is expected that the upward price move will continue.
Once the Buy Stop is reached by the market price it is executed as a market order, at the best available price.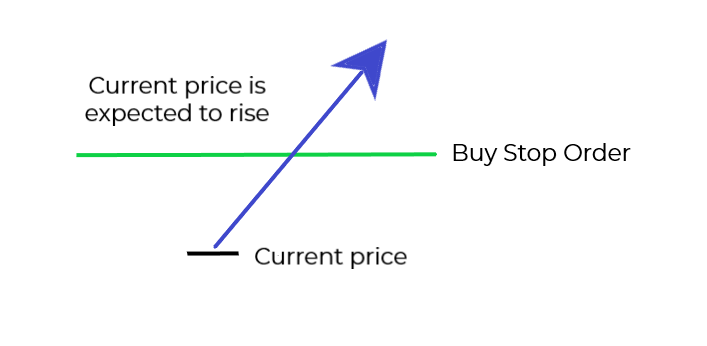
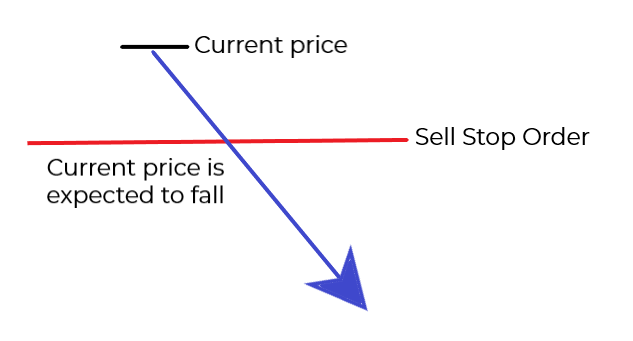
SELL STOP ORDER
The Sell Stop is a pending order used to sell a currency pair (open a short position) at a level, which is below the current price. A Sell Stop order gives instructions to open a short position at a price worse than the currently available.
A typical situation to use the Sell Stop is at a breakout of a support level, when it is expected that the downward movement will continue.
Once the Sell Stop is reached by the market price it is executed as a market order, at the best available price.
TAKE-PROFIT AND STOP-LOSS ORDERS IN THE FOREX MARKET
There are variations of the market orders, that serve for managing the position. These are the Stop-Loss (S/L) and the Take-Profit (T/P). Their main purpose is to limit the losses and protect the profits of an open position.
TAKE-PROFIT ORDER
The Take-Profit order is a variation of the Buy/Sell Limit order, that closes out an open position for a profit. It marks the profit size that the trader expects from that open position.
If the market price rises (in a long position) to the take-profit point, the Take Profit (T/P) order is executed and the position is closed for a profit. If you have an open short position and it is developing well (meaning the price is falling), the T/P order will close the position for a profit, once the take-profit level is reached.
STOP-LOSS ORDER
With a long position, the Stop-Loss defends the buy order, should the price turn the wrong way (down) and reach the level of the S/L order.
If the stop-loss price is reached, the order is triggered and executed at the best available price, thus closing the long position and limiting the losses. Because of its market nature, the execution price is not guaranteed and may incur slippage.
With a short position the Stop-Loss serves to protect the open sell order. If the market price turns the wrong way (up) and touches the stop-loss price, the S/L is triggered and executed at the best available price, thus ending the short position. Because it’s a market order, the execution price is not guaranteed and may incur slippage.
The Take-profit and the Stop-Loss orders should be used together, so that the open position is optimally managed. The difference between the market price and these two points helps define the risk-reward ratio of the trade.
TRAILING STOP ORDER
The Trailing Stop order is similar to the stop-loss order but is more flexible. The stop price of this order is not fixed, instead it moves in relation to the market price. It is set to a fixed percentage or a fixed amount from the market price and as long as the market price moves in the desired direction, the trailing stop order follows (or trails) behind.
If the market price pulls back in the opposite direction, the trailing order stops in place. If the price continues its path and hits the stop, it is executed as a market order.
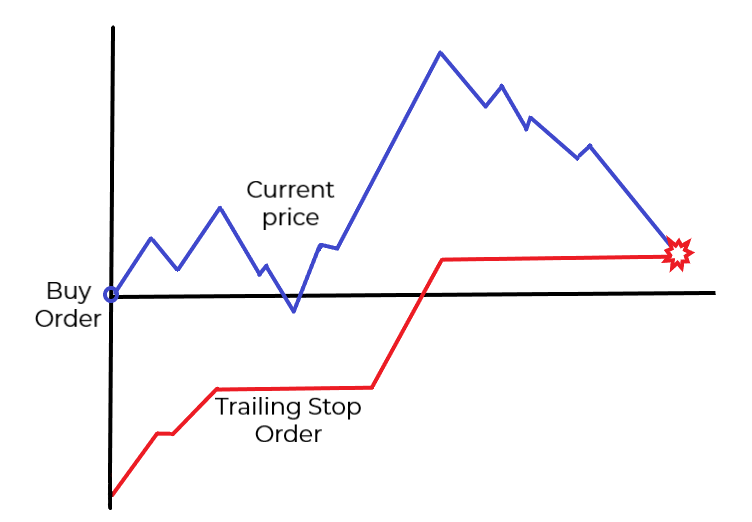
The trailing stop order is placed above the market price to protect a short position and below it when it protects a long position.
It is essential to correctly determine how far away from the market price to set the trailing stop. Putting it too close to the price means any minor correction would trigger the stop and end the position prematurely. Too far away on the other hand means it may never serve its protective purpose.